Create a web API with ASP.NET Core controllers
Introduction
- APS.NET stands for
Active Server Pages Network Enabled Technologies. - It is a server-side web-application framework designed for web development to produce dynamic web pages.
- ASP.NET is cross platform and runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Docker.
- ASP.NET extends the .NET platform with tools and libraries specifically for building web apps.
- ASP.NET Core is the open-source and cross-platform version of ASP.NET.
- ASP.NET allows you to build many types of web applications, including
- web pages,
- REST APIs,
- microservices, and
- hubs that push real-time content to connected clients.
 Web API with ASP.NET Core Demo
Web API with ASP.NET Core Demo
Create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project
- Create a folder for your project.
- Open a terminal and navigate to the project folder.
- Run the following command to create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project:
1
dotnet new webapi -controllers -f net8.0
- This command creates the files for a basic web API project that uses controllers, along with a C# project file returns a list of weather forecasts.
- Web API projects are secured with https by default. If you have problems, configure the ASP.NET Core HTTPS development certificate.
- You might receive a prompt from Visual Studio Code to add assets to debug the project. Select Yes in the dialog.
- The command uses an ASP.NET Core project template aliased as webapi to scaffold a C#-based web API project.
- The folder name I used for the project is
ContosoPizza. - A ContosoPizza directory is created. This directory contains an ASP.NET Core project running on .NET.
- The project name matches the ContosoPizza directory name.
- You should now have access to these files and directories:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
-| Controllers
-| obj
-| Properties
-| appsettings.Development.json
-| appsettings.json
-| ContosoPizza.csproj
-| ContosoPizza.http
-| Program.cs
-| WeatherForecast.cs
- The following table describes the files and directories in the project:
| File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
| Controllers | Contains classes with public methods exposed as HTTP endpoints. |
| Program.cs | Configures services and the app’s HTTP request pipeline, and contains the app’s managed entry point. |
| ContosoPizza.csproj | Contains configuration metadata for the project. |
| ContosoPizza.http | Contains configuration to test REST APIs directly from Visual Studio Code. |
- When you run the project with
dotnet run, it:- Locates the project file at the current directory.
- Retrieves and installs any required project dependencies for this project.
- Compiles the project code.
- Hosts the web API with the ASP.NET Core Kestrel web server at both an HTTP and HTTPS endpoint.
- A port from
5000to5300is selected forHTTP, and from7000to7300for HTTPS, when the project is created. - You can easily change the ports that you use during development by editing the project’s
launchSettings.jsonfile. - You should get output similar to the following, indicating that your app is running:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Building...
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: https://localhost:7294
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: http://localhost:5118
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Application started. Press Ctrl+C to shut down.
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Hosting environment: Development
If you’re running this app on your own machine, you could direct a browser to the HTTPS link displayed in the output (in the preceding case, https://localhost:7294) to view the resulting page.
- Open a browser and navigate to the
WeatherForecastendpoint to see the weather forecast data. - The URL should look like this:
https://localhost:7294/weatherforecast. - You should see JSON output similar to this example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[
{
"date": "2021-11-09T20:36:01.4678814+00:00",
"temperatureC": 33,
"temperatureF": 91,
"summary": "Scorching"
},
{
"date": "2021-11-09T20:36:01.4682337+00:00",
"temperatureC": -8,
"temperatureF": 18,
"summary": "Cool"
}
// ...
]
ASP.NET Core Web API Controllers
- A controller is a public class with one or more public methods known as actions.
- By convention, a controller is placed in the project root’s Controllers directory.
- The actions are exposed as
HTTPendpoints via routing. - So an HTTP GET request to https://localhost:{PORT}/weatherforecast causes the
Get()method of theWeatherForecastControllerclass to be executed.
The base class: ControllerBase
- A controller-based web API consists of one or more controller classes that derive from ControllerBase.
- The web API project template provides a starter controller:
WeatherForecastController. - The
WeatherForecastControllerclass inherits from the ControllerBase base class. - Web API controllers should typically derive from
ControllerBaserather fromController. Controllerderives fromControllerBaseand adds support for views, so it’s for handling web pages, not web API requests.- If the same controller must support views and web APIs, derive from Controller.
- The ControllerBase class provides many properties and methods that are useful for handling HTTP requests.
- This base class provides much standard functionality for handling HTTP requests, so you can focus on the specific business logic for your application.
- Two important attributes are applied to WeatherForecastController, as shown in the following code:
1
2
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]enables opinionated behaviors that make it easier to build web APIs.- Some behaviors include parameter source inference, attribute routing as a requirement, and model validation error-handlingenhancements*.
[Route]defines the routing pattern[controller].- The controller’s name (case-insensitive, without the Controller suffix) replaces the
[controller]token. This controller handles requests to https://localhost:{PORT}/weatherforecast.
The Get() method
WeatherForecastControllerincludes a single controller action, designated by the[HttpGet(Name = "GetWeatherForecast")]attribute.- This attribute routes
HTTP GETrequests to thepublic IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get()method. The method returns anIEnumerable<WeatherForecast>.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[HttpGet(Name = "GetWeatherForecast")]
public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get()
{
return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast
{
Date = DateOnly.FromDateTime(DateTime.Now.AddDays(index)),
TemperatureC = Random.Shared.Next(-20, 55),
Summary = Summaries[Random.Shared.Next(Summaries.Length)]
})
.ToArray();
}
- Other common actions are associated with a web API that performs CRUD operations (GET, PUT, POST, DELETE).
- But an API controller needs to implement only one controller action.
- In this case, you’re getting the full list of
WeatherForecastreturned. - The
GEToperation also allows for retrieving a single item by passing in anidentifier. - In ASP.NET, you can retrieve a single item by using the
[HttpGet("{id}")]attribute.
Add a data store
- Before you start to implement a web API for pizza, you need to have a data store on which you can perform operations.
- You need a
modelclass to represent a pizza in inventory. - The
modelcontains properties that represent the characteristics of a pizza. - The
modelis used to pass data in the web API and to persist pizza options in the data store. - In this unit, that data store is a simple local in-memory caching service.
- In a real-world application, you’d consider using a database, such as SQL Server, with Entity Framework Core.
Create a model
- Create a
Modelsfolder and add a new file calledPizza.cs. - The directory name
Modelsis a convention. - The directory name comes from the model-view-controller architecture that the web API uses.
- Add the following code to Models/Pizza.cs and save your changes. This class defines a pizza.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
namespace ContosoPizza.Models;
public class Pizza
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string? Name { get; set; }
public bool IsGlutenFree { get; set; }
}
Add a service
- A service is a class that contains business logic.
- The service is responsible for processing data and returning the results.
- Create a
Servicesfolder and add a new file calledPizzaService.cs. - Add the following code to
Services/PizzaService.csand save your changes. This class defines a service that manages pizza data.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
using ContosoPizza.Models;
namespace ContosoPizza.Services;
public static class PizzaService
{
static List<Pizza> Pizzas { get; }
static int nextId = 3;
static PizzaService()
{
Pizzas = new List<Pizza>
{
new Pizza { Id = 1, Name = "Classic Italian", IsGlutenFree = false },
new Pizza { Id = 2, Name = "Veggie", IsGlutenFree = true }
};
}
public static List<Pizza> GetAll() => Pizzas;
public static Pizza? Get(int id) => Pizzas.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Id == id);
public static void Add(Pizza pizza)
{
pizza.Id = nextId++;
Pizzas.Add(pizza);
}
public static void Delete(int id)
{
var pizza = Get(id);
if(pizza is null)
return;
Pizzas.Remove(pizza);
}
public static void Update(Pizza pizza)
{
var index = Pizzas.FindIndex(p => p.Id == pizza.Id);
if(index == -1)
return;
Pizzas[index] = pizza;
}
}
- This service provides a simple in-memory data caching service with two pizzas by default.
- Our web API uses that service for demo purposes.
- When you stop and start the web API, the in-memory data cache is reset to the two default pizzas from the constructor of PizzaService.
- The service provides methods to
- get all pizzas,
- get a single pizza by ID,
- add a pizza,
- delete a pizza, and
- update a pizza.
Add a controller
- Create a
Controllersfolder and add a new file calledPizzaController.cs. - Add the following code to
Controllers/PizzaController.csand save your changes. This class defines a controller that manages pizza data.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
using ContosoPizza.Models;
using ContosoPizza.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ContosoPizza.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class PizzaController : ControllerBase
{
public PizzaController()
{
}
// GET all action
// GET by Id action
// POST action
// PUT action
// DELETE action
}
Get all pizzas
- Add the following code to the
PizzaControllerclass to get all pizzas.
1
2
3
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult<List<Pizza>> GetAll() =>
PizzaService.GetAll();
- The preceding action:
- Responds only to the
HTTP GETverb, as denoted by the[HttpGet]attribute. - Returns an
ActionResultinstance of typeList<Pizza>. - The
ActionResulttype is the base class for all action results inASP.NET Core. - Queries the service for all pizza and automatically returns data with a
Content-Typevalue ofapplication/json.
- Responds only to the
Get a pizza by ID
- You can implement another GET action that requires an id parameter.
- You can use the built-in [HttpGet(“{id}”)] attribute to define a method that returns the pizzas from our service.
- The routing logic registers [HttpGet] (without id) and [HttpGet(“{id}”)] (with id) as two different routes.
- You can then write a separate action to retrieve a single item.
- Replace the
// GET by Id actioncomment inControllers/PizzaController.cswith the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public ActionResult<Pizza> Get(int id)
{
var pizza = PizzaService.Get(id);
if(pizza == null)
return NotFound();
return pizza;
}
- The preceding action:
- Responds only to the
HTTP GETverb, as denoted by the[HttpGet]attribute. - Requires that the id parameter’s value is included in the URL segment after
pizza/. Remember, the controller-level[Route]attribute defined the/pizzapattern. - Queries the database for a pizza that matches the provided
idparameter.
- Responds only to the
Test the controller with .http file
- Open ContosoPizza.http
- Add a new
GETto call the Pizza endpoint under the###seperator:
1
2
3
4
GET /pizza/
Accept: application/json
###
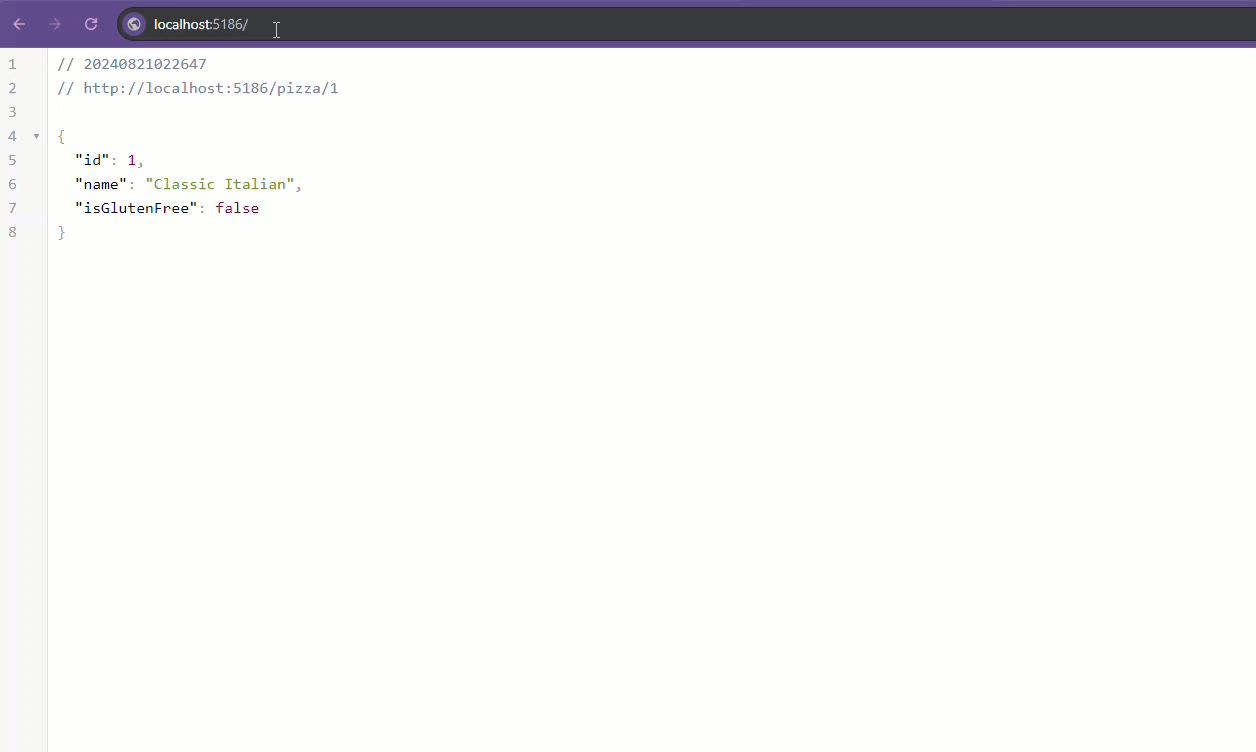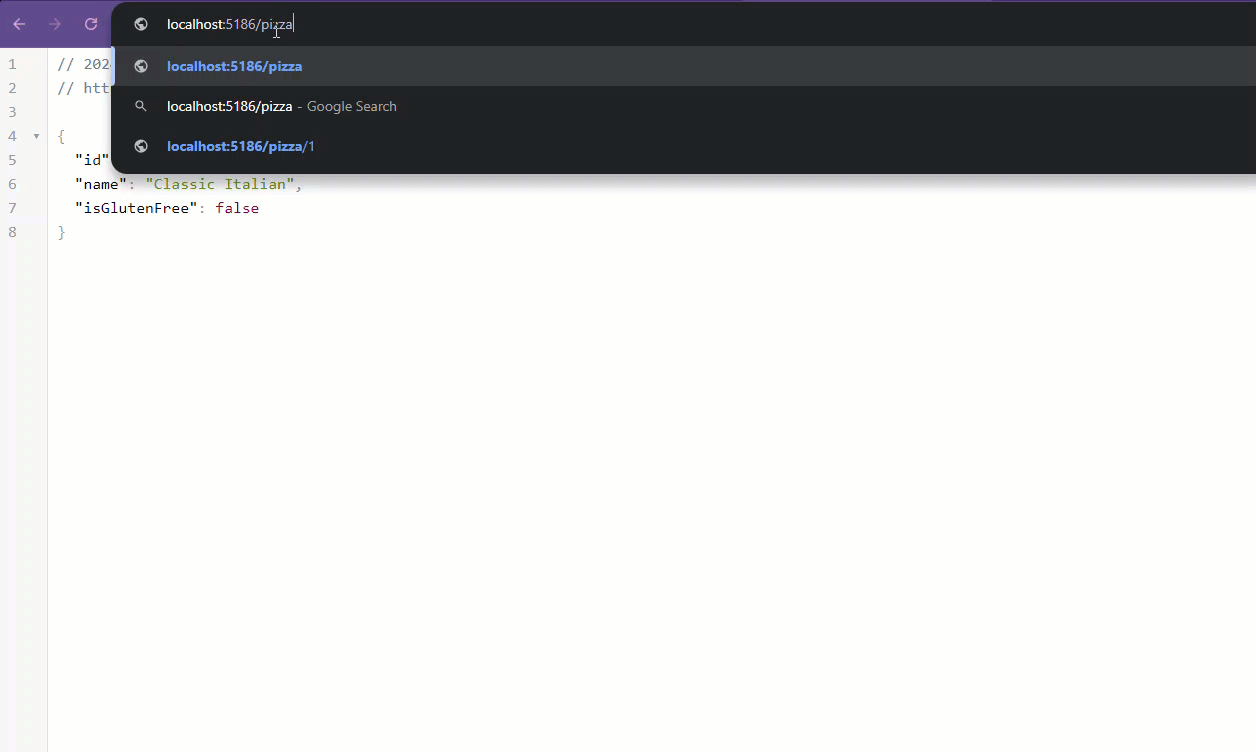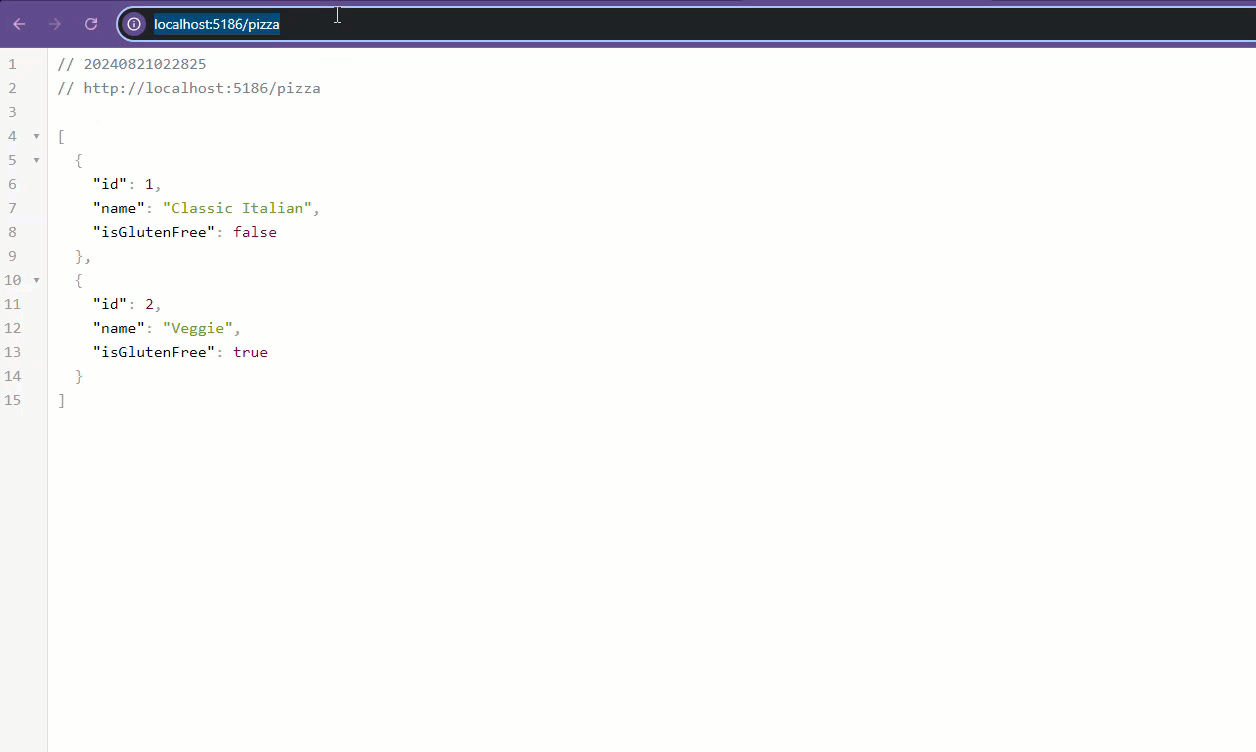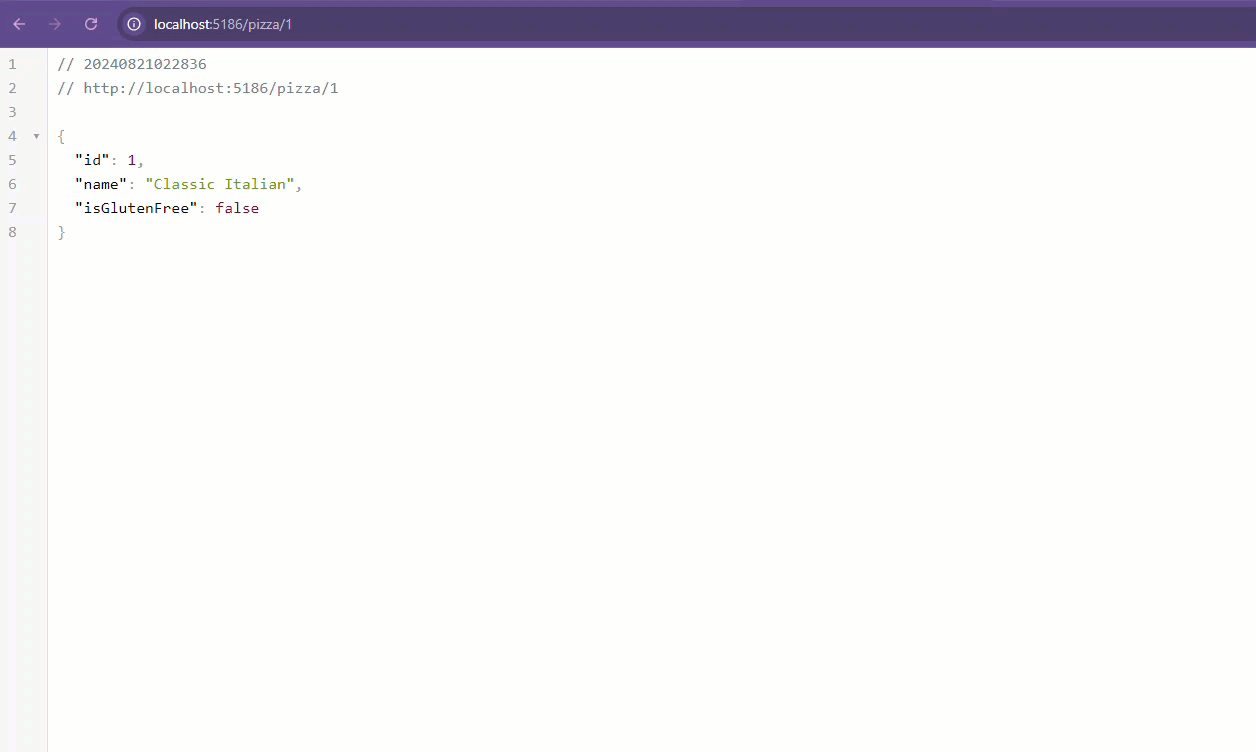
- Visiting the URL
https://localhost:7294/pizza/in the browser should return the list of pizzas. - Likewise, visiting the URL
https://localhost:7294/pizza/1should return the pizza with ID 1.
Add a pizza
- To enable users to add a new item to the endpoint, you must implement the POST action by using the
[HttpPost]attribute. - When you pass the item (in this example, a pizza) into the method as a parameter,
ASP.NET Coreautomatically converts anyapplication/JSONthat’s sent to the endpoint into a populated.NET Pizzaobject. - Here’s the method signature of the Create method that you’ll implement in the next section:
1
2
3
4
5
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Create(Pizza pizza)
{
// This code will save the pizza and return a result
}
- The
[HttpPost]attribute mapsHTTP POSTrequests sent tohttp://localhost:5000/pizzaby using theCreate()method. - Instead of returning a list of pizzas, as we saw with the
Get()method, this method returns anIActionResultresponse. IActionResultlets the client know if the request succeeded and provides theIDof the newly created pizza.IActionResultuses standardHTTPstatus codes, so it can easily integrate with clients regardless of the language or platform they’re running on.- The complete
Create()method is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Create(Pizza pizza)
{
PizzaService.Add(pizza);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), new { id = pizza.Id }, pizza);
}
Update a pizza
- Modifying or updating a pizza in our inventory is similar to the POST method that you implemented, but it uses the
[HttpPut]attribute and takes in the id parameter in addition to the Pizza object that needs to be updated:
1
2
3
4
5
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public IActionResult Update(int id, Pizza pizza)
{
// This code will update the pizza and return a result
}
- The
[HttpPut]attribute mapsHTTP PUTrequests sent tohttp://localhost:5000/pizza/{id}by using theUpdate()method. - The
Update()method takes in theidof the pizza to update and the updatedPizzaobject. - The method returns an
IActionResultresponse, similar to theCreate()method. - The
Update()method updates the pizza in the in-memory cache and returns the updated pizza. - The complete
Update()method is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public IActionResult Update(int id, Pizza pizza)
{
if(id != pizza.Id)
return BadRequest();
var existingPizza = PizzaService.Get(id);
if(existingPizza is null)
return NotFound();
PizzaService.Update(pizza);
return NoContent();
}
Delete a pizza
- One of the easier actions to implement is the DELETE action, which takes in just the id parameter of the pizza to remove from the in-memory cache:
1
2
3
4
5
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int id)
{
// This code will delete the pizza and return a result
}
- A full implementation of the
Delete()method is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int id)
{
var pizza = PizzaService.Get(id);
if(pizza is null)
return NotFound();
PizzaService.Delete(id);
return NoContent();
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.